Welcome to the Hibernate Tutorial Series. In previous tutorial we saw how to implement One to Many relationship using XML mapping. In this tutorial we will modify the source code from previous One To Many XML mapping tutorial and add JPA/Annotation support to it.
1. Database Setup
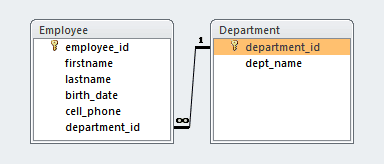
For this example, we will use MySQL database. Create following two tables in MySQL. Note that Employee and Department table exhibits One-to-many relationship. Each Department can be associated with multiple Employees and each Employee can have only one Department.
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`department_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`dept_name` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`department_id`)
)
COLLATE='latin1_swedish_ci'
ENGINE=InnoDB
ROW_FORMAT=DEFAULT
AUTO_INCREMENT=115
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`employee_id` BIGINT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`firstname` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`lastname` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`birth_date` DATE NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`cell_phone` VARCHAR(15) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`department_id` BIGINT(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`),
INDEX `FK_DEPT` (`department_id`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_DEPT` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `department` (`department_id`)
)
COLLATE='latin1_swedish_ci'
ENGINE=InnoDB
ROW_FORMAT=DEFAULT
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2. Project Setup
Download the source code: Hibernate-one-to-many-set-example.zip (9 KB) and import the project in Eclipse. We will update the source code.
3. Update Maven Dependency
File: pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>HibernateCache</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateCache</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<description></description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>ejb3-persistence</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-annotations</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)3. Remove Hibernate Mapping (hbm) Files
We are not going to use hibernate mapping files or hbm files as we will map the model using Java 5 Annotations. Delete the files employee.hbm.xml and department.hbm.xml.
4. Update Hibernate Model Class
File: Employee.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import java.sql.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="EMPLOYEE")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="employee_id")
private Long employeeId;
@Column(name="firstname")
private String firstname;
@Column(name="lastname")
private String lastname;
@Column(name="birth_date")
private Date birthDate;
@Column(name="cell_phone")
private String cellphone;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="department_id")
private Department department;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstname, String lastname, String phone) {
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastname = lastname;
this.birthDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
this.cellphone = phone;
}
// Getter and Setter methods
}
Code language: Java (java)@ManyToOne annotation defines a single-valued association to another entity class that has many-to-one multiplicity. It is not normally necessary to specify the target entity explicitly since it can usually be inferred from the type of the object being referenced.
@JoinColumn is used to specify a mapped column for joining an entity association.
File: Department.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="DEPARTMENT")
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="DEPARTMENT_ID")
private Long departmentId;
@Column(name="DEPT_NAME")
private String departmentName;
@OneToMany(mappedBy="department")
private Set<Employee> employees;
// Getter and Setter methods
}
Code language: Java (java)@OneToMany annotation defines a many-valued association with one-to-many multiplicity.
If the collection is defined using generics to specify the element type, the associated target entity type need not be specified; otherwise the target entity class must be specified.
The association may be bidirectional. In a bidirectional relationship, one of the sides (and only one) has to be the owner: the owner is responsible for the association column(s) update. To declare a side as not responsible for the relationship, the attribute mappedBy is used. mappedBy refers to the property name of the association on the owner side. In our case, this is passport. As you can see, you don’t have to (must not) declare the join column since it has already been declared on the owners side.
5. Update Hibernate Configuration File
File: hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password"></property>
<property name="connection.pool_size">1</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<property name="cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.NoCacheProvider</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">validate</property>
<mapping class="net.viralpatel.hibernate.Department"/>
<mapping class="net.viralpatel.hibernate.Employee"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)6. Review Project Structure
Once all the source files are in place, the project structure should looks like below:
7. Execute example
Execute following Main.java file which will create one Department and two Employees.
File: Main.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
public class Main {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sf.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Department department = new Department();
department.setDepartmentName("Sales");
session.save(department);
Employee emp1 = new Employee("Nina", "Mayers", "111");
Employee emp2 = new Employee("Tony", "Almeida", "222");
emp1.setDepartment(department);
emp2.setDepartment(department);
session.save(emp1);
session.save(emp2);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
Code language: Java (java)Output:
Hibernate: insert into DEPARTMENT (DEPT_NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into EMPLOYEE (firstname, lastname, birth_date, cell_phone, department_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into EMPLOYEE (firstname, lastname, birth_date, cell_phone, department_id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Thus we saw in above example how to implement One to Many relationship in Hibernate using Annotation. Also we used java.util.Set for our example.
8. One- To Many Bi-directional Indexed mapping
Above example was pretty straightforward. We mapped multiple employees with a department. For this we used java.lang.Set. But the order in which the employees are mapped with department is not conserved. What if you have a requirement where you want to preserve order for entities that you save.
We can use java.util.List to map ordered entities. For this first we will need to add a column IDX in Employee table which will store the index value.
8.1 Modify Employee table
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`employee_id` BIGINT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`firstname` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`lastname` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`birth_date` DATE NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`cell_phone` VARCHAR(15) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`department_id` BIGINT(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`idx` INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`),
INDEX `FK_DEPT` (`department_id`),
CONSTRAINT `FK_DEPT` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `department` (`department_id`)
)
COLLATE='latin1_swedish_ci'
ENGINE=InnoDB
ROW_FORMAT=DEFAULT
AUTO_INCREMENT=33
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)8.2 Modify Hibernate Model classes
Update Employee.java and Department.java model classes and add the list support. Also note that we are changing the annotations.
File: Department.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.IndexColumn;
@Entity
@Table(name="DEPARTMENT")
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="DEPARTMENT_ID")
private Long departmentId;
@Column(name="DEPT_NAME")
private String departmentName;
@OneToMany(cascade={CascadeType.ALL})
@JoinColumn(name="department_id")
@IndexColumn(name="idx")
private List<Employee> employees;
// Getter and Setter methods
}
Code language: Java (java)Note that in Department entity class, we removed mappedBy clause from @OneToMany. This mark Department as the relationship owner and make it responsible to update foriegn keys and index values.
Also we specified index coulmn using @IndexColumn annotation to specify which column in Employee table we would like to store index in.
File: Employee.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import java.sql.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="EMPLOYEE")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
@Column(name="employee_id")
private Long employeeId;
@Column(name="firstname")
private String firstname;
@Column(name="lastname")
private String lastname;
@Column(name="birth_date")
private Date birthDate;
@Column(name="cell_phone")
private String cellphone;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="department_id",
insertable=false, updatable=false,
nullable=false)
private Department department;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstname, String lastname, String phone) {
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastname = lastname;
this.birthDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
this.cellphone = phone;
}
// Getter and Setter methods
}
Code language: Java (java)8.3 Execute List example
File: Department.java
package net.viralpatel.hibernate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
public class Main {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sf = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sf.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Department department = new Department();
department.setDepartmentName("Sales");
Employee emp1 = new Employee("Nina", "Mayers", "111");
Employee emp2 = new Employee("Tony", "Almeida", "222");
department.setEmployees(new ArrayList<Employee>());
department.getEmployees().add(emp1);
department.getEmployees().add(emp2);
session.save(department);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
Code language: Java (java)Output:
Hibernate: insert into DEPARTMENT (DEPT_NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into EMPLOYEE (birth_date, cell_phone, firstname, lastname) values (?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into EMPLOYEE (birth_date, cell_phone, firstname, lastname) values (?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: update EMPLOYEE set department_id=?, idx=? where employee_id=?
Hibernate: update EMPLOYEE set department_id=?, idx=? where employee_id=?
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)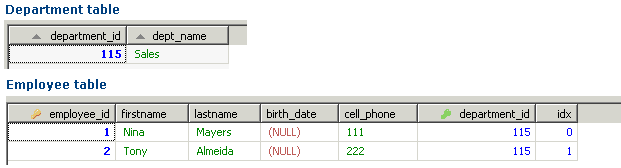
Download Source Code
Hibernate-One-To-Many-Annotation-Set.zip (8 KB)
Hibernate-One-To-Many-Annotation-List.zip (8 KB)


Just landed on your tutorials and they look very detailed interesting …
Will start following them in the next days (weeks) … thank you for your efforts =))
Very detailed and simple to understand
yes that’s right
Please share the Department.setEmployees() method. Without that, I don’t see a way for an Employee to know what to which Department it belongs. I’m assuming that the method will look like this:
This is convience method is it necessary in this senario ?
Hi Viral,
First of all, Thanks for detail tutorial. Can you please add samples to retrieve information from DB with varoius cases one-one, one-many, Many-one.
Thanks
Plz some one tell me How i use one to many mapping in hibernate for creation of three tables.
1.discussion(discId,queId,ansId)
2.question(queId,question,postdate)
3.answer(ansId,answer,postDate)
Thanks in advance
Plz rply its argent
when using this code in dynamic project of struts2 i get following error..
:-
Could not determine type for: java.util.Set, at table: UserDetails, for columns: [org.hibernate.mapping.Column(questionSet)]
Hi Mandar,
Are you using field access strategy for annotating your entity properties? i.e. Are you adding annotations on class fields or to getter methods?
Check if you using only one access strategy and not mixing up both.
HI,
The example are very help full for learning new technology in java.I m following and it is very understanding .I need front end design of screen with back end data using GWT .It is my humble request to send me tutorial of gwt using hibernate frame work
Thanks Vinayak. I have not written tutorial on GWT with Hibernate, but I hope to write soon. Please subscribe for articles via email so you don’t miss any future tutorials.
Hi viral,It s nice tutorial.please give this examples using webapplication then it uses
Very useful examples. Please provide some more examples if possible.
Hi Viral, Thanks for detailed explanation….Can we do this mapping with a single entity class using @SecondaryTable.
(NOTE: I need both primary keys to be inserted using the single entity class itself )
department_employee table is also generated without any data please explain this and why the content is null ??
Hello Viral,
Thanks a lot for such a work. You deserve accolades. I have one question. When I run above example, the table and data get populated, However, when I run it next time, I expect the data should be inserted one more time and not update. I have done the required changes into the hibernate file. Please help. I am using MySQL with autoincrement as ID.
Thanks in advance.
Excellent website I ever found self explanatory ,good work keep it up .Thanks
Hi all,
In the above example both the colum names are used as “department_id” . All I want to know illustrate an example where the column names are different but still primary and foreign key mapping exists.
OR
Is it mandatory to maintain same name for such colums?
Thanks for the article :)
For the One- To Many Bi-directional Indexed mapping, I’m having real difficulties in implementing delete such that when I delete an employee from the department, he should be deleted from the table too.
I’ve come across this solution : http://dinukaroshan.blogspot.com/2011/09/hibernate-by-example-part-1-orphan.html but I’m still looking for a solution which doesn’t need a join table.
hi all ..
I want to know how to run this sample…
I do Run Java application and then appear the Select Java Application box ..
I don’t know which one I choose ..
so I need help .. :(
pls reply for me..
Hi Viral,
In the One- To Many Bi-directional Indexed mapping section, the annotation on department, @JoinColumn(name=”department_id”, insertable=false, updatable=false, nullable=false).
I think ‘nullable=false’ should be removed. It works in your example because the db schema has already been generated. Should the db schema automatically be generated by Hibernate, it would cause a ConstraintViolation Exception.
Hi Viral,
I have a same application but different tables. I am fetching the data using left join.
Query query = session.createQuery(“FROM DrugList as p LEFT JOIN p.vers c WHERE p.drugListKey=’1′”);
DrugList drugList = (DrugList) query.uniqueResult();
I am getting the below exception.
SEVERE: Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcher] in context with path [/CampaignManagementWorkstation] threw exception [Request processing failed; nested exception is org.hibernate.exception.SQLGrammarException: ORA-00904: “VERS1_”.”DRUGLISTKEY”: invalid identifier
] with root cause
java.sql.SQLException: ORA-00904: “VERS1_”.”DRUGLISTKEY”: invalid identifier
The query generated from Hibernate is: Hibernate: select druglist0_.drug_list_key as drug1_0_0_, vers1_.drug_list_version_key as drug1_1_1_, druglist0_.channel_type as channel2_0_0_, druglist0_.description as descript3_0_0_, druglist0_.drug_list_id as drug4_0_0_, druglist0_.EFF_DATE as EFF5_0_0_, druglist0_.enter_date as enter6_0_0_, druglist0_.entered_by as entered7_0_0_, druglist0_.EXP_DATE as EXP8_0_0_, druglist0_.last_update_date as last9_0_0_, druglist0_.last_updated_by as last10_0_0_, druglist0_.type_id as type11_0_0_, vers1_.drugListKey as drugList3_1_1_, vers1_.version_number as version2_1_1_ from CWS_DRUG_LIST druglist0_ left outer join cws_drug_list_version vers1_ on druglist0_.drug_list_key=vers1_.drugListKey where druglist0_.drug_list_key=4
The Java Bean classes are
I would appreciate your reply asap.
Thanks
hi,
i want to know what is the use of Indexcolumn annoatation ,Orderby, NaturalId annotations in hibernate.
please help me.
waiting for ur reply…
I really like this series. Appreciated.
However, for my situation, this example did not work, because fields insertable, updatable and nullable are given, all with value false. In my situation, the following worked:
Keep up the good work!
@JoinColumn(name=”department_id”)
Ha! The missing ingredient to my test mapping, I kept getting an error telling me a column didn’t exist, adding this (or @JoinColumn(name=”user_id”) for me) sorted it.
Funny no other demo seems to use this annotation.
Cheers for the great and detailed demo.
Awesome tutorial.:)
this very usefull for me, i’ll keep learn from this blog
thanks.,
Hi,
I have downloaded and used your code for annotation of one to many relationship. but I got the following error while persisting the department object.
15:11:01,559 ERROR SqlExceptionHelper:144 – Field ‘department_id’ doesn’t have a default value.
I have modified the generated value as below:
Could you guide me how to resolve this problem.
I am using MySQL 5.5 as db.
Thanks,
Maria.
Getting an error. Kindly see what may be the possible cause –
log4j:WARN No appenders could be found for logger (org.hibernate.cfg.annotations.Version).
log4j:WARN Please initialize the log4j system properly.
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at com.hk.hibernate.OneToMany.OneToManyMain.main(OneToManyMain.java:14)
Caused by: org.hibernate.AnnotationException: @OneToOne or @ManyToOne on com.hk.hibernate.OneToMany.Employee.dept references an unknown entity: com.hk.hibernate.OneToMany.Department
at org.hibernate.cfg.FkSecondPass.doSecondPass(FkSecondPass.java:56)
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.processFkSecondPassInOrder(AnnotationConfiguration.java:428)
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.secondPassCompile(AnnotationConfiguration.java:286)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1283)
at com.hk.hibernate.basic.HibernateUtil.(HibernateUtil.java:17)
… 1 more
Please put a simple Example using hibernet with annotation using Netbeans.
I am New to Hibernet.
Hi Viral,
I appreciate the effort you put in writing these examples, thanks for that.
Coming to your example on OneToMany association in hibernate
for the same example can you show how to use a @JoinTable with emply_id and dept_id columns.
Also which method is efficient in case of OneToMany association
1. To use Two tables (as in your example)
2. To use a third table which is a cross reference from employee and department having emp_id and dept_id.
Hi Viral,
I am designing a hospital management system where I have the following entities and tables
1. Doctor
2. Specialization
The Specialization table contains master data.
One doctor can be specialized in many, so I have a @OneToMany association of Specialization in Doctor entity, it is a unidirectional association and Specialization will not contain Doctor entity
So for mapping doctor to specializations I have created third table doctor_specializations.
In case I want to delete a specialization from database how should I do
1. First delete all the rows from the table doctor_specializations and finally delete in the table specialization.
2. Is there any way that removes all the associated rows from database when I just remove a row in specialization.
Also suggest the better designing for the above if it is not good.
hii Viral, could u plz provide any project related to Hibernate and struts 1.2 ..
Sir I am new in hibernate.Plz post one example with struts2+hibernate one to many mapping demo…..This type of example is not in anywahere plz post it..
Regards Pardeep
In any application, there will be employees already present how to deal with this situation. Here in this example you are creating a new object every time.
Thats great post Viral,
How can I implement the HQL for this example ?
thanks
In my case it is working only if i am adding below lines in main program:
emp1.setDepartment(department); // Required to save department id in employee table
emp2.setDepartment(department);
session.save(emp1); // Required to save recoed in employee table
session.save(emp2);
Kindly let me know if it was missed or it should work only with session.save(department);. As department has reference of employee objects.
If I am adding above lines Records get saved only in department table.
Very good examples
Thank you..
Really enjoyed your examples. Very easy to follow.
Thank you very much for your effort.
am new to thiss…
INFO: Bind entity net.viralpatel.hibernate.Employee on table EMPLOYEE
Initial SessionFactory creation failed.java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.hibernate.cfg.SecondPass.doSecondPass(Ljava/util/Map;)V
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.buildSessionFactory(HibernateUtil.java:18)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.(HibernateUtil.java:8)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.Main.main(Main.java:13)
Caused by: java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.hibernate.cfg.SecondPass.doSecondPass(Ljava/util/Map;)V
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.processFkSecondPassInOrder(AnnotationConfiguration.java:499)
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.secondPassCompile(AnnotationConfiguration.java:304)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1205)
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.buildSessionFactory(AnnotationConfiguration.java:859)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.buildSessionFactory(HibernateUtil.java:15)
… 2 more
log4j:WARN No appenders could be found for logger (org.hibernate.type.BasicTypeRegistry).
log4j:WARN Please initialize the log4j system properly.
Initial SessionFactory creation failed.org.hibernate.HibernateException: Missing column: dept_name in RBI.DEPARTMENT
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.buildSessionFactory(HibernateUtil.java:16)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.(HibernateUtil.java:8)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.Main.main(Main.java:10)
Caused by: org.hibernate.HibernateException: Missing column: dept_name in RBI.DEPARTMENT
at org.hibernate.mapping.Table.validateColumns(Table.java:276)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.validateSchema(Configuration.java:1343)
at org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaValidator.validate(SchemaValidator.java:139)
at org.hibernate.impl.SessionFactoryImpl.(SessionFactoryImpl.java:378)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1872)
at net.viralpatel.hibernate.HibernateUtil.buildSessionFactory(HibernateUtil.java:13)
… 2 more
Hi
Can you please help me in
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/18895585/hibernate-version-annotation-and-object-references-an-unsaved-transient-instanc
hi viral,
how to fetch data from multiple table using hibernate select clause in Struts2 + hibernate framework ??
As well as how to display in jsp page using iterator tag??
hi when i use session.update so instead of getting updated a new row is getting added , i want the existing row to get updated
It was really helpful….aewsome and simple….
I used same annotation in my project for manytoone mapping. I have exisitng entry for department andthen trying to enter employee but it through folowwing error
org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (constraint)
and
Caused by: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException: Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails( Constraint)
Please help if posible
hi i am getting error for similar example
Oct 31, 2013 7:09:38 PM org.hibernate.annotations.common.Version
INFO: HCANN000001: Hibernate Commons Annotations {4.0.2.Final}
Oct 31, 2013 7:09:38 PM org.hibernate.Version logVersion
Oct 31, 2013 7:09:39 PM org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration doConfigure
INFO: HHH000041: Configured SessionFactory: null
four
Oct 31, 2013 7:09:39 PM org.hibernate.service.jdbc.connections.internal.DriverManagerConnectionProviderImpl configure
WARN: SQL Error: 515, SQLState: 23000
Oct 31, 2013 7:09:40 PM org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.spi.SqlExceptionHelper logExceptions
ERROR: Cannot insert the value NULL into column ‘SVR_ID’, table ‘Service.dbo.SERVICE_REQUESTS’; column does not allow nulls. INSERT fails.
Exception in thread “main” org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: could not execute statement
at org.hibernate.exception.internal.SQLStateConversionDelegate.convert(SQLStateConversionDelegate.java:129)
at org.hibernate.internal.SessionImpl.save(SessionImpl.java:752)
at com.modal.demo.main(demo.java:32)
Caused by: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: Cannot insert the value NULL into column ‘SVR_ID’, table ‘Service.dbo.SERVICE_REQUESTS’; column does not allow nulls. INSERT fails.
at com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException.makeFromDatabaseError(SQLServerException.java:216)
Hi, Check your table SERVICE_REQUESTS. I guess the SVR_ID is primary key and while inserting values in this table hibernate did not generate one and hence the error. Check if you have correctly configured @GeneratedValue with svrId column in your model.
Thanks for the cool tutorial post.
very well explained.. !! thanks
Thank you very much for the tutorial! It worked well, altough I had to change “Column” to “JoinColumn” at manyToOne for department.
hi viral,
thank for tutorial,
but in select query join columns are coming and it giving me error
How to insert values of two different table into another table….please help..using struts-2 hibernate mapping.
Smallestsweetest exaple ine the world love u sir
Hi Viral and all,
can someone please resolve my problem of mapping one to many relationship between a primary key and a composite key.
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/24609861/hibernate-mapping-one-to-many-relation-ship-between-primary-key-and-composite-ke
ur post saved my day,
thank u
what is the use of mappedby??if we will not specify then what will happen???
read this:
http://viralpatel.net/hibernate-many-to-many-annotation-mapping-tutorial/
“EMPLOYEE_MEETING” separate table has been created. If we wont specify “mappedBy”, the another table will create with the name MeetingEmployee. But we have already created “EMPLOYEE_MEETING”. To restrict the duplicate table creation, we are telling hibernate to not to create because its already created by “meetings”.
Hi
How save foreign key in employee table?
thanks
why is it that when you update the non owning entity .. then update the owning entity, the update on the non owning entity will not take effect ??
is it because of the cascadetypes??
what would be the appropriate cascade type for this kind of problem??
should i use merge not update ??
how ??
good article!
can any one tell how to the above application in a spring mvc application using hibernate
thankssss buddy
Thanks Viral Nice posts.
Viral, thank you very much for this post! It was just what I wanted!
Hi Viral…
I have faced a issues while test one-many bi directional mapping .
please assist what to do.
Thank you.
@Entity
@Table(name=”customers”)
public class Customer
{
// One Customer can place many order
// One order belongs to one custmer
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name=”cid”)
int cid;
@Column(name=”cname”)
String cname;
@Column(name=”email”)
String email;
@Column(name=”dob”)
Date dob;
@Column(name=”phone”)
Long phone;
@OneToMany(mappedBy=”customer”)
Set orders;
@Entity
@Table(name=”orders”)
public class Order {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name=”orderId”)
int orderId;
@Column(name=”totalQty”)
int totalQty;
@Column(name=”totalCost”)
Double totalCost;
@Column(name=”orderDate”)
Date orderDate;
@Column(name=”status”)
String status;
@JoinColumn(name=”cid”, referencedColumnName=”cid”)
Customer customer;
Ecception :
———————————
org.hibernate.MappingException: Could not determine type for: anno.association.mapping.one2many.bidirectional.Customer, for columns: [org.hibernate.mapping.Column(customer)]
at org.hibernate.mapping.SimpleValue.getType(SimpleValue.java:266)
at org.hibernate.mapping.SimpleValue.isValid(SimpleValue.java:253)
at org.hibernate.mapping.Property.isValid(Property.java:185)
at org.hibernate.mapping.PersistentClass.validate(PersistentClass.java:410)
at org.hibernate.mapping.RootClass.validate(RootClass.java:192)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.validate(Configuration.java:1026)
at org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration.buildSessionFactory(Configuration.java:1211)
at org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration.buildSessionFactory(AnnotationConfiguration.java:915)
at anno.association.mapping.one2many.bidirectional.HibernateUtilAnno.(HibernateUtilAnno.java:15)
at anno.association.mapping.one2many.bidirectional.CMLab27.main(CMLab27.java:19)
java.lang.NullPointerException
at anno.association.mapping.one2many.bidirectional.CMLab27.main(CMLab27.java:20)
why declaring private Set employees? (Is this here only to indicate the relationship specified?)
I tried to get the employees in the department variable, but it returned null,
mast likha hain VIRAL bhai. your blogs are really getting viral
sir both table carry department_id as column so it is bit confusinf can u make it as fk_department_id in the other table
How to remove relationship after declaring it, without effecting the other programs?
Hi, Here is Named query made to fetch track .
{
“SELECT t FROM Track t LEFT JOIN FETCH t.metadata tm WHERE t.id= :id AND tm.userID = :userID”
}
In Track entity i am having metadata list with @OneToMany relationship with join table inbetween name = tracks_metadata_join.
{
//TrackMetadata
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, targetEntity=TrackMetadata.class, orphanRemoval = true)
@JoinTable(name = “tracks_metadata_join”, joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = “track_id”,
referencedColumnName = “id”, table = “tracks”) }, inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(
name = “track_metadata_id”, referencedColumnName = “id”, table = “tracks_metadata”))
@JsonProperty
private List metadata = new ArrayList();
}
The result of above query is Track with all it’s all metadata, But i want Track with particular metadata. like user specific.
Thanks!
Thanks for nice and clear explanation.
Thanks Santosh
Very Simple and Clear Explanation, Thanks for posting like this viral
How passport is the OWNER of the bidirectional relationship? Check the text as “In our case, this is passport”
Hello, I have been following your tutorials. i get a java.lang. stackoverflowerror error each time i run an update. i am using hibernate and spring. do you have a solution to it? thanks
As per your example suppose I want to show or display employee first name, last name, and their department name so how I can write that query in HQL format
This is the best example across many other sites and works correctly but the entities department-employee cannot hold 1-n relationship, they always have n-n relationship.